Operating CCTV cameras effectively requires understanding their features and functionalities. Firstly, familiarize yourself with the camera’s controls, including pan, tilt, and zoom options. Ensure the camera is properly connected to a power source and recording device.
Next, adjust camera settings such as resolution, frame rate, and motion detection sensitivity to suit your surveillance needs. Position the camera strategically to cover the desired area while minimizing blind spots. Regularly clean the lens to maintain clear image quality.

Additionally, consider using a secure password for remote access to prevent unauthorized viewing or tampering. Finally, regularly check camera feeds and recordings to monitor activity and identify any potential security issues. This article aims to provide a comprehensive guide on how to operate cctv camera. By following these outlines, you can effectively operate CCTV cameras to enhance security and surveillance in your home or business.
Importance of Understanding CCTV Camera Operation
Understanding the operation of CCTV cameras is crucial for maximizing their effectiveness in enhancing security and surveillance. Proper knowledge of how to operate these devices not only ensures their optimal performance but also extends their lifespan through appropriate maintenance and handling.
Furthermore, a comprehensive understanding helps in effectively responding to security breaches or incidents by enabling quick access to relevant footage and efficient use of camera functionalities like zoom and tilt to capture crucial details.
Additionally, skilled operation can assist in deterring criminal activity, as well-managed surveillance systems are recognized as a powerful preventative measure. In essence, being adept in CCTV camera operation empowers individuals and organizations to protect assets, ensure safety, and maintain peace of mind.
Explanation of Camera Controls
Among the most critical aspects of operating CCTV cameras is understanding the camera controls, which enable the operator to adjust the field of view and focus on specific areas. The primary controls include:
- Pan: This control allows the camera to move horizontally, enabling it to cover a wider area from left to right. Panning is especially useful for surveillance of large areas, as it can follow movements across a broad scene.
- Tilt: Tilt functionality permits the camera to move vertically, up and down, providing a better view of objects at different heights or the ground below. This control is indispensable for adjusting the camera’s angle to capture the desired area effectively.
- Zoom: Zoom controls adjust the camera’s lens to bring distant objects into closer view without moving the camera itself. There are two types of zoom – optical and digital. Optical zoom adjusts the camera lens to change the focal length, maintaining the image quality, while digital zoom crops the image to focus on specific areas, which can sometimes reduce clarity.

Understanding and mastering these controls are essential for effective surveillance, as they directly influence the camera’s ability to capture clear and comprehensive footage of the monitored area. By adeptly managing pan, tilt, and zoom, operators can ensure their CCTV systems provide the maximum security coverage.
Familiarization with Camera Settings and Configuration Options
Beyond mastering the basic controls of pan, tilt, and zoom, effective CCTV operation also involves understanding and adjusting camera settings to optimize performance for various environments and situations. Key settings and configuration options include:
- Resolution: This determines the clarity and detail of the footage captured by the camera. Higher resolution settings result in clearer images, which are crucial for identifying faces or license plates. However, they also require more storage space and processing power.
- Frame Rate: The frame rate, measured in frames per second (fps), affects the smoothness of video playback. Higher frame rates provide smoother footage but consume more storage space. Adjusting this setting depends on the monitoring needs and storage capacity.
- Motion Detection Sensitivity: This feature allows the camera to trigger recording or send alerts when motion is detected in its field of view. Adjusting the sensitivity level is essential to balance between avoiding false alarms and ensuring all movements are captured.
- Night Vision: For effective surveillance in low-light conditions, explore the camera’s night vision or infrared settings. These options improve the camera’s ability to capture clear footage at night or in poorly lit areas.
- Field of View: The camera’s field of view setting determines the width of the area it can capture. Some cameras offer wide-angle lenses that are ideal for covering large areas, while others may be adjusted to focus on narrower zones for more detailed surveillance.
Each of these settings plays a critical role in tailoring the CCTV system to meet specific surveillance goals and conditions. Regularly reviewing and adjusting these options ensures the system remains effective over time, adapting to any changes in the surveillance environment or requirements.
10 Methods How to Operate CCTV Camera
Method 1: Powering On and Off the CCTV Camera
Properly powering on and off CCTV cameras is essential for their longevity and performance. We’ll provide step-by-step instructions for safely turning on and shutting down CCTV cameras, including troubleshooting tips for power-related issues.
Method 2: Adjusting Camera Settings for Optimal Performance
Configuring camera settings is key to achieving the desired surveillance outcomes. We’ll discuss how to adjust image quality settings such as resolution, frame rate, and exposure, as well as customize motion detection and alarm triggers for efficient monitoring.
Method 3: Controlling Camera Movement (Pan, Tilt, Zoom)
CCTV cameras equipped with pan, tilt, and zoom (PTZ) capabilities offer greater flexibility in surveillance. We’ll explore how to operate PTZ functions to adjust camera direction, focus on specific areas of interest, and track moving objects for comprehensive coverage.
Method 4: Monitoring Live Video Feeds
Accessing live video feeds from CCTV cameras allows real-time monitoring of surveillance areas. We’ll guide users through the process of viewing live video feeds, navigating camera views, and adjusting display settings for optimal viewing experience.

Method 5: Recording and Playback Features
Recording and playback features enable the capture and review of surveillance footage for investigation and analysis. We’ll explain how to initiate manual recording sessions, schedule automatic recording modes, and retrieve recorded footage using playback controls.
Method 6: Remote Access and Monitoring
Remote access to CCTV cameras via web interface or mobile app enables monitoring from anywhere with an internet connection. We’ll discuss how to set up remote access, monitor live video feeds, and access recorded footage remotely, along with security considerations for remote access.
Method 7: Advanced Camera Features (Night Vision, Wide Dynamic Range)
Exploring advanced camera features such as night vision and wide dynamic range (WDR) enhances surveillance capabilities in challenging lighting conditions. We’ll delve into the settings and functionality of these features to optimize camera performance.
Method 8: Integrating CCTV Cameras with Other Security Devices
Integrating CCTV cameras with other security devices such as alarms and access control systems enhances overall security management. We’ll discuss integration options, compatibility considerations, and customization settings for seamless integration.
Method 9: Customizing Integration Options for Enhanced Security and Automation
Customizing integration options allows users to tailor CCTV camera operation to their specific security needs and preferences. We’ll explore advanced integration features, automation scenarios, and programming options for maximizing security effectiveness.
Method 10: Troubleshooting and Maintenance
Identifying and resolving operational issues is essential for maintaining CCTV camera performance. We’ll provide troubleshooting tips and solutions for common issues, along with recommendations for regular maintenance practices to ensure optimal camera operation.
Proper Shutdown Procedures to Avoid Damage
Ensuring the proper shutdown of your CCTV system is crucial to avoid potential damage and prolong the life of your equipment. To safely shut down a CCTV camera, follow these step-by-step instructions:

- Access the CCTV System’s Interface: Log into the CCTV system’s management software on your computer or mobile device. This is where you will initiate the shutdown process.
- Navigate to the System Settings or Power Options: Look for a section labeled “System Settings,” “Power Options,” or something similar within the interface. This area controls the power settings for your CCTV system.
- Initiate the Shutdown Process: Select the option to “Shutdown” or “Turn Off” the system. Confirm your selection if prompted. This will safely power down your CCTV cameras and the recording unit, ensuring all current operations are properly closed and no data is lost.
- Physically Disconnect the Power Source (if necessary): Once the system has completed its shutdown process, and if directed by the manufacturer’s guidelines, you may then physically disconnect the power source. This step is crucial during extended periods of inactivity or when maintenance is required.
- Follow Manufacturer’s Specific Instructions: Always consult the user manual or manufacturer’s guidelines for any specific instructions related to your particular CCTV model. Adhering to these instructions ensures that you’re following the best practices for your equipment.
By following these proper shutdown procedures, you can help avoid unnecessary damage to your CCTV system, ensuring it remains in optimal condition for continuous surveillance and security.
Troubleshooting Common Power-Related Issues
Power-related issues in CCTV systems can lead to unexpected downtime and reduce the effectiveness of your surveillance efforts. Identifying and solving these issues promptly ensures that your CCTV system remains operational and effective. Here are some common power-related issues and how to troubleshoot them:
No Power to CCTV Cameras:
- Check the Power Supply: Ensure the power supply is connected properly and the outlet is functioning. Use a multimeter to verify the voltage output.
- Inspect Power Cables: Look for any visible damage to the cables. Replace any faulty cables to restore power to the camera.
- Secure Connections: Loose connections can cause intermittent power loss. Check all connections are tight and secure.

- Evaluate Power Adapter: An inadequate power supply or a failing power adapter can lead to power fluctuations. Test with a replacement adapter to rule out this issue.
- Check Power Requirements: Ensure that the power supply unit (PSU) can handle the load of all connected devices. Overloading can cause the PSU to fail.
- Distribute Power Load: If necessary, distribute the cameras across multiple power supply units to prevent overloading.
- Cable Length: Long cable runs can cause voltage drops. Consider using a power booster or switch to a higher gauge cable for longer distances.
- Check Connections: Corroded or loose connections can also contribute to voltage drops. Inspect and clean all connections.
- Surge Protection: Use surge protectors to safeguard your CCTV system against power surges that can damage sensitive electronics.
- Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS): Implementing a UPS can provide backup power and protect against surges, ensuring continuous operation.
By systematically addressing these common power-related issues, you can reduce downtime and extend the life of your CCTV system. Regularly inspecting power supplies, cables, and connections as part of routine maintenance will help prevent these issues from occurring.
Adjusting Camera Settings for Optimal Performance
To achieve the best performance from your CCTV cameras, adjusting their settings to suit specific conditions and requirements is paramount. Proper tuning can enhance image quality, ensure efficient storage management, and improve overall surveillance effectiveness. Here are key settings to focus on for optimal performance:
Resolution Settings: Adjust the camera resolution to find the right balance between image quality and storage space. Higher resolution offers more detail but consumes more storage.
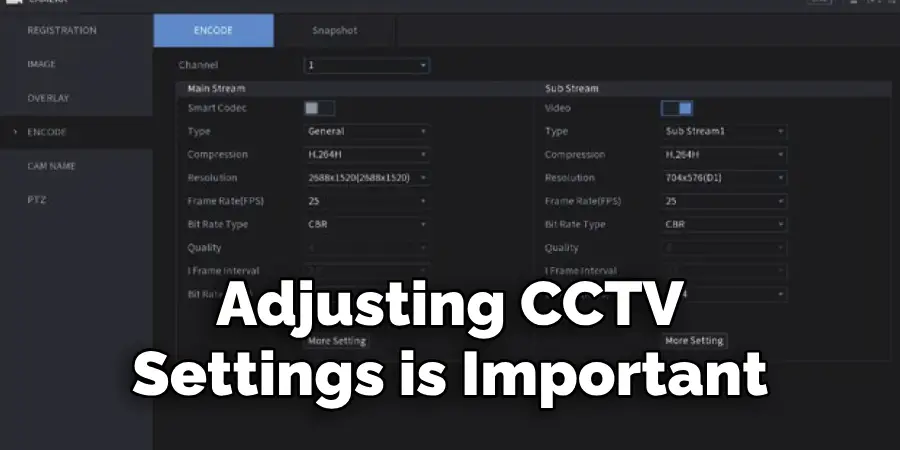
Frame Rate Configuration: Configure the frame rate according to the surveillance needs. A higher frame rate ensures smoother footage but requires more bandwidth and storage. Reducing the frame rate can save storage space and bandwidth without significantly compromising the surveillance quality in low-activity areas.
Light Sensitivity Settings: Adjust the light sensitivity or day/night settings to improve the camera’s performance in varying lighting conditions. Enabling features like Wide Dynamic Range (WDR) can help balance the light in scenes with both very bright and very dark areas.
Motion Detection Sensitivity: Fine-tune motion detection settings to reduce false alarms and ensure that recordings are triggered by actual security events. Adjusting the sensitivity and specifying motion detection zones can focus the surveillance on relevant areas.
Backlight Compensation: Enable backlight compensation to improve visibility in conditions where the background is much brighter than the foreground. This is crucial for capturing identifiable images of subjects when facing strong light sources.
Privacy Masks: Use privacy masks to block out areas within the camera’s field of view that you don’t want to record, such as neighboring properties or public sidewalks, to maintain privacy and comply with regulations.
Focus and Zoom: Manually or automatically adjust the focus and zoom settings to ensure clear images of areas of interest. For cameras with optical zoom capabilities, finding the right zoom level can provide detailed visuals of critical areas without sacrificing quality.
By carefully adjusting these camera settings, users can significantly improve the efficiency, effectiveness, and reliability of their CCTV surveillance system. Regular reviews and adjustments in response to changes in the monitored environment will contribute to maintaining optimal performance.
Controlling Camera Movement
To enhance surveillance coverage and flexibility, controlling camera movement is an essential capability in many CCTV systems. PTZ (Pan, Tilt, Zoom) cameras offer dynamic control over camera movement and focus, allowing operators to adjust the camera’s field of view remotely to monitor different areas or focus on specific incidents. Here’s how to effectively control camera movement:
Pan and Tilt: PTZ cameras can pan (move horizontally) and tilt (move vertically), providing a 360-degree overview of their surroundings. Control these movements through your CCTV system’s interface, opting for preset patrols or manually adjusting the view as required.

Zoom: Use zoom functionality to get a closer look at distant objects or areas of interest. PTZ cameras offer optical zoom capabilities without loss of image quality, making them ideal for detailed surveillance.
Preset Positions: Most PTZ cameras allow operators to save preset positions for quick access. These presets can be configured for areas that require regular monitoring, enabling swift adjustments to the camera’s view with a single command.
Patrol Sequences: For comprehensive surveillance, set up patrol sequences that automatically move the camera between preset positions at specified intervals. This ensures continuous coverage of key areas without manual intervention.
Auto-Tracking: Some advanced PTZ cameras feature auto-tracking. This technology enables the camera to automatically pan, tilt, and zoom to follow moving objects or persons within its field of view, providing continuous monitoring of suspicious activities.
Remote Control: Utilize remote control capabilities through desktop software, mobile apps, or web interfaces. This flexibility allows security personnel or authorized users to control camera movements from anywhere, enhancing the system’s responsiveness to incidents.
Integration with Motion Detection: Combine camera movement control with motion detection features to automatically direct the camera towards areas where motion is detected, ensuring you capture critical moments without delay.
By mastering the control of camera movement, operators can significantly increase the effectiveness of their surveillance system, ensuring comprehensive coverage and the ability to dynamically respond to security events as they happen.

Conclusion
By mastering these ten comprehensive methods for operating CCTV cameras, users can effectively monitor and manage their surveillance systems for enhanced security and peace of mind. Whether adjusting camera settings, controlling camera movement, accessing live video feeds, or integrating with other security devices, each method contributes to a comprehensive approach to CCTV operation.
With the knowledge and guidance provided in this guide, users can confidently navigate the complexities of CCTV camera operation and maximize the effectiveness of their surveillance efforts. Be sure to follow all instructions on how to operate cctv camera carefully, and always consult an expert when in doubt.

